In modern industry and infrastructure, many of the most dangerous failures begin quietly. An oil tank slowly approaches its capacity limit, an engine temperature rises beyond safe operation, or lubrication levels drop without visible signs. These situations rarely announce themselves dramatically. Instead, they are detected by sensors, working continuously in the background, long before human operators can perceive the risk. In oil storage and transportation systems, level and flow sensors monitor oil movement around the clock. When abnormal levels or unexpected flow patterns appear, sensors immediately trigger warnings or automatic shutdowns. In countless real-world cases, these early alerts have prevented oil overflows and spills, protecting surrounding environments, waterways, and communities from severe and long-lasting damage.
Inside engines and industrial machinery, temperature sensors act as an early warning system against overheating. An engine running under excessive load or insufficient lubrication can fail within minutes. Sensors detect abnormal heat buildup and prompt corrective actions such as activating cooling systems or stopping the equipment altogether. These interventions not only save costly machinery but also protect workers from fire hazards and mechanical failures.
Lubrication systems rely heavily on flow and pressure sensors to ensure moving components receive the protection they need. When lubricant delivery becomes insufficient or irregular, sensors alert maintenance teams before friction causes irreversible damage. This enables predictive maintenance, repairs carried out before breakdowns occur, keeping operations efficient and workers safe.
In hazardous environments, gas sensors provide life-saving protection by detecting invisible threats. Toxic or combustible gases often accumulate without warning, but sensors recognize dangerous concentrations instantly. When thresholds are exceeded, alarms sound, ventilation systems activate, and evacuation procedures begin. Many lives have been saved because sensors reacted faster than human senses ever could.
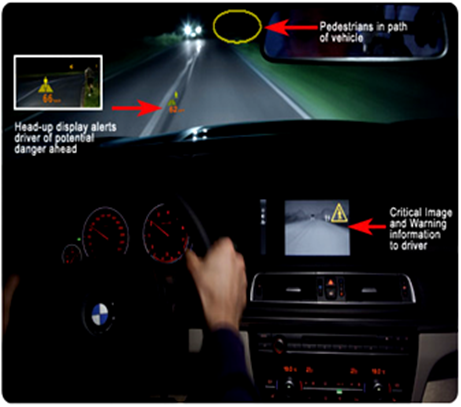
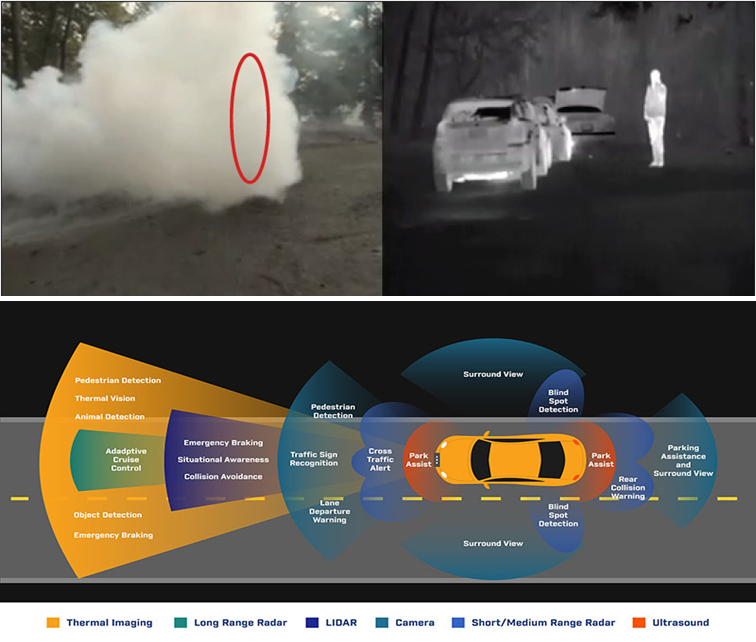
Visibility can disappear in seconds during fog, smoke, or darkness, yet infrared sensors continue to see. Thermal imaging systems detect heat signatures rather than visible light, allowing vehicles, security systems, and rescue teams to identify people, obstacles, and equipment in conditions where human vision fails. In emergency response situations, infrared sensing has helped locate survivors and prevent accidents when time and clarity are critically limited.
Sensors rarely draw attention when everything is operating smoothly. They work silently, constantly measuring, analyzing, and protecting. But when danger arises, their value becomes undeniable. From preventing environmental disasters and mechanical failures to safeguarding human lives, sensors stand as quiet guardians, ensuring safety, reliability, and trust in an increasingly complex world.
Process Monitoring and Control
Thermopile sensors are widely used in industrial automation for non-contact temperature measurement, allowing continuous monitoring of hot surfaces, moving components, and hazardous environments. Unlike contact-based sensors, thermopile sensors measure temperature without physical interaction, reducing wear and ensuring reliable operation in high-temperature or contaminated areas. These sensors are commonly applied in furnaces, production lines, and equipment monitoring systems to detect overheating, optimize process parameters, and prevent unexpected failures.
Gas Detection and Safety Systems
Gas sensors, including CO₂ and other gas-detection technologies, play a critical role in industrial safety and environmental control. They monitor gas concentrations in confined spaces, production facilities, and storage areas to prevent hazardous buildup and ensure compliance with safety regulations. In automated systems, gas sensor data is integrated into control units that trigger alarms, ventilation systems, or shutdown procedures, helping to protect personnel and equipment.
Flow Measurement and Process Efficiency
Flow sensors are essential for controlling and optimizing the movement of gases and fluids in industrial processes. Accurate flow measurement ensures correct material delivery, stable process conditions, and efficient resource utilization.
In industries such as manufacturing, chemical processing, and energy production, flow sensors support automated dosing, leak detection, and system balancing, helping reduce waste and improve operational efficiency.
Pressure Monitoring and Equipment Protection
Pressure sensors and digital pressure gauges provide critical feedback for pneumatic and hydraulic systems. Continuous pressure monitoring enables automated control systems to maintain optimal operating conditions and detect abnormal pressure fluctuations early. By identifying potential issues before failures occur, pressure sensing contributes to reduced downtime, improved equipment lifespan, and enhanced workplace safety.
Quality Control and Predictive Maintenance
Advanced sensing technologies support predictive maintenance strategies by detecting early signs of equipment degradation. Temperature, flow, and pressure trends are analyzed to identify abnormal patterns, allowing maintenance teams to address issues proactively. This data-driven approach improves production reliability, minimizes unplanned downtime, and reduces overall maintenance costs.
Driving Smart and Connected Factories
As industrial automation evolves toward smart and connected factories, sensors form the foundation of intelligent systems. By enabling real-time data collection and seamless integration with control networks, sensors support automation, digitalization, and continuous improvement initiatives across industrial operations.