Sensor technology has evolved dramatically over the past decades, transforming from simple signal-detecting components into intelligent, high-precision systems that influence nearly every aspect of modern life. At Precision Sensors Design, we stand at the intersection of this evolution, combining advanced engineering, automated manufacturing, and application-driven innovation to deliver sensing solutions that are accurate, reliable, and scalable.
The Evolution of Sensors: From Components to Intelligent Systems
Early sensors were limited by manual assembly, inconsistent performance, and narrow application scope. Today’s sensors are the result of highly optimized design, advanced materials, and automated manufacturing, enabling unprecedented levels of precision and repeatability.
Modern sensor development begins with simulation-driven design, where thermal, electrical, and mechanical behaviors are modeled before physical production. This approach allows engineers to predict performance, reduce noise, and improve long-term stability. As sensors become smaller, faster, and more integrated, manufacturing accuracy becomes just as critical as design innovation.
Precision Manufacturing at Scale
The ability to manufacture millions of sensors with consistent performance is made possible through smart die bonding, wire bonding, and hermetic capping machines. These advanced systems operate with micron-level precision, ensuring accurate placement of sensor dies, reliable electrical connections, and stable mechanical structures.
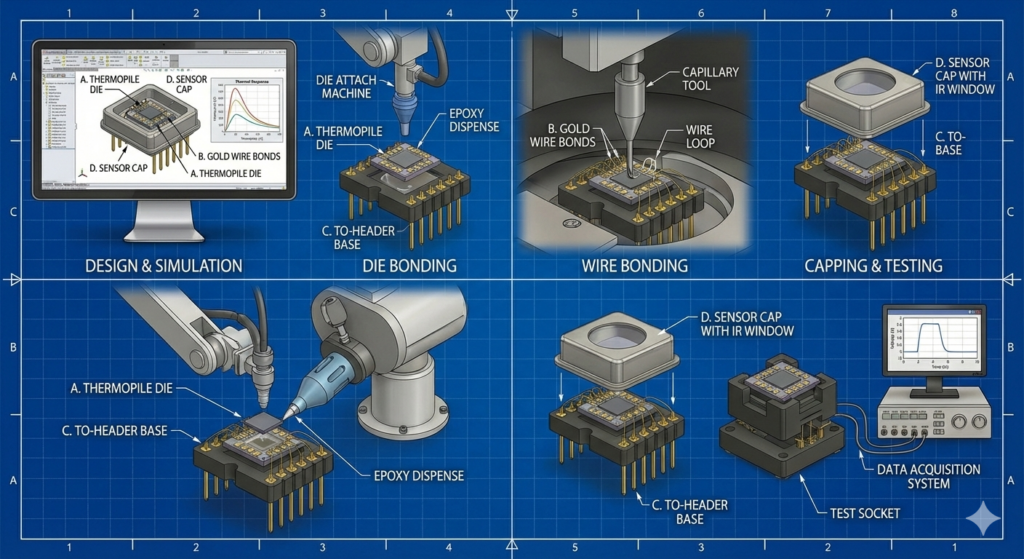
- Die bonding machines ensure uniform thermal and mechanical contact, critical for sensors such as thermopiles and flow sensors where heat transfer accuracy directly affects performance.
- Smart wire bonding systems create reliable electrical interconnections with optimized loop profiles, minimizing signal loss and ensuring durability under thermal cycling.
- Automated hermetic capping machines, using air or nitrogen environments, seal sensitive components to protect against moisture, oxidation, and contamination.
This level of automation ensures not only production efficiency but also repeatability, quality control, and long-term reliability across high-volume manufacturing.
Thermopile Sensors: From Defense to Medical Applications
Thermopile sensors are a prime example of how sensing technology has expanded across industries. By converting infrared radiation into electrical signals, thermopile sensors enable non-contact temperature measurement, making them indispensable in diverse applications.

Defense and Security
Thermopile sensors are used in thermal detection systems for night vision, perimeter monitoring, and equipment overheating detection. Their ability to detect temperature differences without direct contact makes them reliable in harsh and sensitive environments.
Medical and Healthcare
In medical devices, thermopile sensors enable accurate, hygienic temperature measurement in infrared thermometers, patient monitoring systems, and diagnostic equipment. During health screenings, non-contact thermopile sensors allow rapid and safe temperature checks, reducing the risk of cross-contamination.
Industrial and Consumer Applications
Thermopile sensors are also widely used in industrial process monitoring, smart home devices, and energy management systems—detecting heat loss, monitoring equipment performance, and improving efficiency.
Flow Sensors: Improving Efficiency and Safety
Flow sensors play a critical role in controlling and optimizing the movement of gases and fluids. In daily life, they are commonly found in:
- Medical ventilators and respiratory devices, ensuring accurate airflow delivery
- Industrial process control systems, monitoring gas flow for safety and efficiency
- Smart appliances, such as gas meters and HVAC systems, to optimize energy consumption
By providing real-time flow data, these sensors help prevent waste, improve system performance, and enhance operational safety.
CO₂ Sensors: Enhancing Air Quality and Sustainability
CO₂ sensors have become essential in modern living environments. They are widely used in:
- Smart buildings, where they regulate ventilation systems to maintain healthy indoor air quality
- Schools and offices, ensuring safe CO₂ levels for productivity and well-being
- Greenhouses, where CO₂ monitoring optimizes plant growth and agricultural efficiency
- Industrial safety systems, detecting gas buildup in confined spaces
By enabling intelligent air management, CO₂ sensors contribute directly to energy savings, improved health, and environmental protection.
Sensors as Enablers of a Sustainable Future
Sensors do more than collect data—they enable smarter decisions that protect the environment and improve industrial efficiency. Accurate sensing helps reduce energy waste, detect leaks and inefficiencies, prevent equipment failure, and minimize emissions.
For example:
- Thermopile sensors detect heat loss in buildings, reducing energy consumption
- Flow sensors identify gas leaks before they become hazardous
- CO₂ sensors optimize ventilation to balance air quality with energy efficiency
Through these applications, sensing technology plays a vital role in building safer industries, healthier environments, and more sustainable systems.
Driving Innovation Forward
At Precision Sensors Design, we believe innovative sensing technology is built on precision, reliability, and real-world impact. By continuously advancing sensor design, manufacturing automation, and application expertise, we empower our customers to develop intelligent products that improve lives, protect resources, and shape the future.
